Difference between revisions of "Booster Adapter"
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
| image=Booster Adapter BA-100 (1) (smaller).png}} | | image=Booster Adapter BA-100 (1) (smaller).png}} | ||
| − | + | ==Overview== | |
<p>As the name implies, the Booster Adapter is a product which can be used to adapt different manufacturers' boosters (and command stations) together. This product is intended to offer you, the user, a quick and easy way to "plug and play" with your command station and boosters. Whether you are upgrading your booster network, command station, or both, the Booster Adapter can help make your update quick and painless! | <p>As the name implies, the Booster Adapter is a product which can be used to adapt different manufacturers' boosters (and command stations) together. This product is intended to offer you, the user, a quick and easy way to "plug and play" with your command station and boosters. Whether you are upgrading your booster network, command station, or both, the Booster Adapter can help make your update quick and painless! | ||
<p>The Booster Adapter has several on-board plug and terminal connections for: | <p>The Booster Adapter has several on-board plug and terminal connections for: | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
The BA-100 can also provide power for other LCC devices distributed around your layout using the on-board barrel jack and an external 15V power supply (not included). | The BA-100 can also provide power for other LCC devices distributed around your layout using the on-board barrel jack and an external 15V power supply (not included). | ||
| − | + | ==Included In Package== | |
*BA-100 Booster Adapter board x1 | *BA-100 Booster Adapter board x1 | ||
*Option Jumpers x4 | *Option Jumpers x4 | ||
| − | + | ==Physical Interfaces== | |
The Booster Adapter has a few notable physical features: | The Booster Adapter has a few notable physical features: | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
#Configuration Jumpers (see details below) | #Configuration Jumpers (see details below) | ||
#Two RJ-11 4-Pin jacks (for use with NCE Control Bus) | #Two RJ-11 4-Pin jacks (for use with NCE Control Bus) | ||
| − | #Two RJ-12 | + | #Two RJ-12 6-Pin jacks (for use with LocoNET<sup>®</sup> / L.NET-B) |
#Two "LCC" RJ-45 jacks (1x Front: For T-50; 2x Rear for LCC Bus) | #Two "LCC" RJ-45 jacks (1x Front: For T-50; 2x Rear for LCC Bus) | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|DCC Polarity | |DCC Polarity | ||
| − | | | + | |These jumpers may be rotated in order to flip the track output phase of the DCC signal between the LCC bus and the Control Bus / L.NET-B. This will result in the track output phase of Control Bus / L.NET-B boosters being flipped relative to boosters on the LCC bus. This is useful when mixing LCC boosters such as the CS-105 and B-106 if a short circuit is observed crossing between LCC and non-LCC booster boundaries as an alternative to manually flipping the track wiring at the booster track outputs. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
|LCC Power | |LCC Power | ||
| − | | | + | |This pair of jumpers determines how power will be routed between the LCC RJ-45 jacks (Pin 8 in the LCC-CAN Standard S-9.7.1.1). The '''Pass''' setting connects pin 8 of the two LCC jacks together so that power passes between them. The '''Output''' setting disconnects pin 8 from passing between the two LCC jacks and requires and external 15VDC power supply in order to feed up to 400mA of current independently into each LCC jack. |
| − | ''The | + | |} |
| − | + | == Additional Information == | |
| − | + | === Booster Common === | |
| − | + | TCS always recommends for users to provide a booster common whenever two or more boosters are in use. This is especially important for boosters that are not electrically isolated. More information can be found on the [[Booster Interface]] page under [[#Booster_Common|Booster Common]]. | |
| − | + | === Booster Interface === | |
| + | Additional information can be found on the [[Booster Interface]] page. | ||
Revision as of 19:05, 25 October 2022
| Booster Adapter | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Contents
Overview
As the name implies, the Booster Adapter is a product which can be used to adapt different manufacturers' boosters (and command stations) together. This product is intended to offer you, the user, a quick and easy way to "plug and play" with your command station and boosters. Whether you are upgrading your booster network, command station, or both, the Booster Adapter can help make your update quick and painless!
The Booster Adapter has several on-board plug and terminal connections for:
- LCC CAN-Bus
- NCE "Control Bus"
- Digitrax "LocoNet-B"
- Lenz
Some use cases include:
- Connecting a CS-105 to NCE Booster(s)
- Connecting a CS-105 to Digitrax Booster(s)
- Connecting a CS-105 to Lenz Booster(s)
- Connecting a Digitrax command station to NCE Booster(s) (and vice versa)
- Connecting a NCE command station to TCS Booster(s)
- And many more combinations!
The BA-100 can also provide power for other LCC devices distributed around your layout using the on-board barrel jack and an external 15V power supply (not included).
Included In Package
- BA-100 Booster Adapter board x1
- Option Jumpers x4
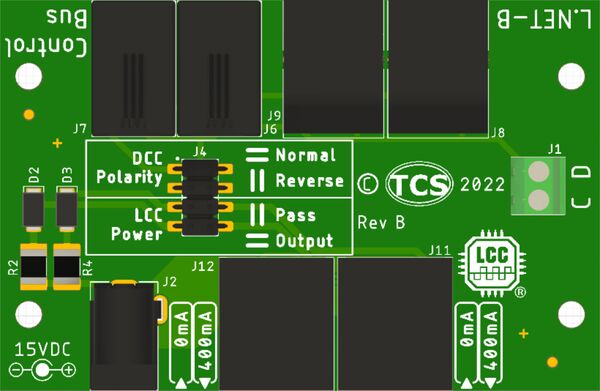
Physical Interfaces
The Booster Adapter has a few notable physical features:
- Green 2-pin screw terminal
- 2.5mm x 5.5mm barrel jack for Power In
- Configuration Jumpers (see details below)
- Two RJ-11 4-Pin jacks (for use with NCE Control Bus)
- Two RJ-12 6-Pin jacks (for use with LocoNET® / L.NET-B)
- Two "LCC" RJ-45 jacks (1x Front: For T-50; 2x Rear for LCC Bus)
Configuration Jumpers
Refer to the table below for information on the configuration jumpers available on the Booster Adapter:
| Jumper Position | Description |
|---|---|
| DCC Polarity | These jumpers may be rotated in order to flip the track output phase of the DCC signal between the LCC bus and the Control Bus / L.NET-B. This will result in the track output phase of Control Bus / L.NET-B boosters being flipped relative to boosters on the LCC bus. This is useful when mixing LCC boosters such as the CS-105 and B-106 if a short circuit is observed crossing between LCC and non-LCC booster boundaries as an alternative to manually flipping the track wiring at the booster track outputs. |
| LCC Power | This pair of jumpers determines how power will be routed between the LCC RJ-45 jacks (Pin 8 in the LCC-CAN Standard S-9.7.1.1). The Pass setting connects pin 8 of the two LCC jacks together so that power passes between them. The Output setting disconnects pin 8 from passing between the two LCC jacks and requires and external 15VDC power supply in order to feed up to 400mA of current independently into each LCC jack. |
Additional Information
Booster Common
TCS always recommends for users to provide a booster common whenever two or more boosters are in use. This is especially important for boosters that are not electrically isolated. More information can be found on the Booster Interface page under Booster Common.
Booster Interface
Additional information can be found on the Booster Interface page.